import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
np.random.seed(12356)
df = pd.read_csv('titanic.csv')
# Drop all the missing values NA
df = df.dropna()Gradient Boosting
1. Predicting Survived
1.1 Import the data
1.2 Assign input and output variabble
# Assign input variables
X = df.loc[:,['Pclass','Sex','Age','Fare','Embarked','SibSp','Parch']]
# Assign target variable
y = df['Survived']1.3 Handle some missing and fix variables types
# Replace missing values by the median
X["Age"] = X["Age"].fillna(X["Age"].median())
# Impute the Embarked variable
X["Embarked"] = X["Embarked"].fillna("S")
# Change Pclass to categorical variable
X['Pclass'] = X['Pclass'].astype(object)1.4 Encode categorical variable
X = pd.get_dummies(X)1.5 Split the data
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.3)1.6 Setup and Train a gradient Boosting
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifier
r1 = GradientBoostingClassifier(n_estimators=100, learning_rate=1)
r1.fit(x_train, y_train)
ypred_test = r1.predict(x_test)
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
mat = confusion_matrix(ypred_test, y_test)
print('===============')
print('Confusion Matrix:')
print(mat)
print('===============')
print('Testing Accuracy:')
print(mat.diagonal().sum()/mat.sum())
print('===============')===============
Confusion Matrix:
[[13 3]
[ 4 35]]
===============
Testing Accuracy:
0.8727272727272727
===============Variable Importance
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
sorted_idx = (-r1.feature_importances_).argsort()
feature_importance = pd.DataFrame({'Variables':x_train.columns[sorted_idx], 'Importance':r1.feature_importances_[sorted_idx]})
df = feature_importance[:10]
df.sort_values('Importance',inplace=True)
df.plot(kind='barh',y='Importance',x='Variables', legend=False)<Axes: ylabel='Variables'>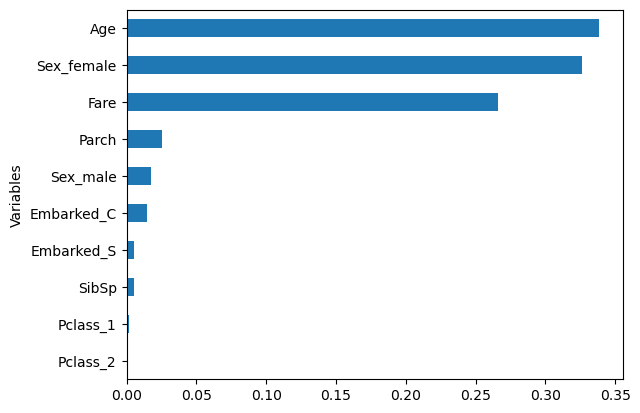
Learning Rate
# Plot the Training Accuracy of gradient boosting with n_estimators running from n1 to n2
# and two learning rates l1 and l2.
n1 = 1
n2 = 100
l1 = .1
l2 = 1
ac = pd.DataFrame([], columns=list(['Rounds','Learning Rate','Accuracy']))
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
for rs in range(n1, n2):
for lr in [l1, l2]:
boost = GradientBoostingClassifier(n_estimators=rs, learning_rate=lr)
boost.fit(x_train,y_train)
ac = pd.concat([ac, pd.DataFrame([[rs, lr, boost.score(x_train,y_train)]],
columns=list(['Rounds','Learning Rate','Training Accuracy']))],
ignore_index=True)
import seaborn as sns; sns.set()
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
ax = sns.lineplot(x="Rounds", y="Training Accuracy",
hue =ac['Learning Rate'].astype('category'),data=ac)
ax.text(x=0.5, y=1.1, s='Learning fast vs. Learning slow',
fontsize=16, weight='bold', ha='center', va='bottom', transform=ax.transAxes)Text(0.5, 1.1, 'Learning fast vs. Learning slow')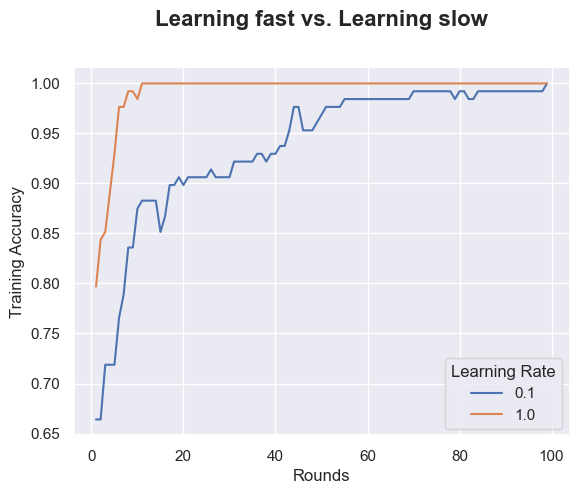
# Plot the Training Accuracy of gradient boosting with n_estimators running from n1 to n2
# and two learning rates l1 and l2.
n1 = 1
n2 = 100
l1 = .1
l2 = 1
ac = pd.DataFrame([], columns=list(['Rounds','Learning Rate','Accuracy']))
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
for rs in range(n1, n2):
for lr in [l1, l2]:
boost = GradientBoostingClassifier(n_estimators=rs, learning_rate=lr)
boost.fit(x_train,y_train)
ac = pd.concat([ac, pd.DataFrame([[rs, lr, boost.score(x_test,y_test)]],
columns=list(['Rounds','Learning Rate','Test Accuracy']))],
ignore_index=True)
import seaborn as sns; sns.set()
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
ax = sns.lineplot(x="Rounds", y="Test Accuracy",
hue =ac['Learning Rate'].astype('category'),data=ac)
ax.text(x=0.5, y=1.1, s='Learning fast vs. Learning slow',
fontsize=16, weight='bold', ha='center', va='bottom', transform=ax.transAxes)Text(0.5, 1.1, 'Learning fast vs. Learning slow')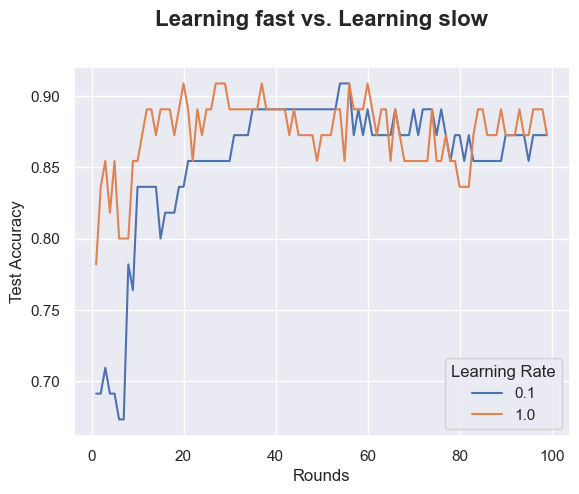
2. Practice
Predicting Breast Cancer.
Import the breast cancer dataset. The data can be downloaded at this link
Set the input (X) and output (y) (Use
df.columnsto see all the columns to easier copy/paste). Split the data into 60% training and 40% testingTrain a gradient boosting model with 200 n_estimators and .1 learning rare. What is testing accuracy of the gradient boosting?
What is the most important variable according to the above gradient boosting model in predicting breast cancer?
Find a gradient boosting (try a few different of
n_estimatorsandlearning_rate) that have a higher testing accuracy than the above gradient boosting. What is the n_estimators and learning of this gradient boosting?